The development of renewable energy sources has gained momentum worldwide. In this regard, there are signs that a hydrogen-fuelled economy holds potential to replace dependence on fossil fuels.
However as appealing as this prospect appears, some barriers to change exist. The predominant challenges to realise a genuine hydrogen economy include:
Viable hydrogen production;
Hydrogen storage and transport; and
Safe utilisation of hydrogen.
Solving these challenges depends greatly on the nature and extent of innovations that must occur. In this insight, the state of development worldwide is examined, with a specific focus on Australia – a potential hydrogen leader – in tackling the above three challenges, with the use of patent filings as an innovation indicator.
Worldwide filings: The state of innovation
There has been a ‘rekindled’ active interest in hydrogen since around the year 2000, with the number of patent families filed increasing every year for six years until 2006.

From 2006, a drop in the number of filings was experienced until about 2011. Yet, filing numbers in 2011 were still significantly higher than those from 2000, with approximately a 97% jump. In the period from 2016 to 2019, patents were filed at a prolific rate over the world (except in Australia), with 2019 representing a 182% increase compared with 2000.
Worldwide applicants
Of the top 20 filers, nearly 77 % of all worldwide filings belong to Asian companies or institutes. Of this, Japan has the edge with nearly 55% of the top 20 filers – Toyota, Honda and Panasonic together own around 7,740 patent families. South Korea follows Japan with 2,574 patent families and the ‘big three’ of Samsung, Hyundai and LG are the country’s main patent holders.

European companies account for about 17% of the top 20 filers with Renault leading the pack. Surprisingly, the top 20 has only one US company – General Motors – with about 685 patent families. These figures indicate that Japanese companies are the hydrogen economy’s leading players, and suggests that Australia’s plan to export massive amounts of ammonia to Japan are a step in the right direction. For reference, ammonia is easier to ship and can be ‘split’ to make hydrogen for fuel cells.
Top filing countries
Although Japanese companies appear to be the front-runners by number, the country with the greatest volume of applications being filed is China. The Chinese government has promoted this shift through various programmes, although no analysis has been undertaken to assess the quality of such patents.
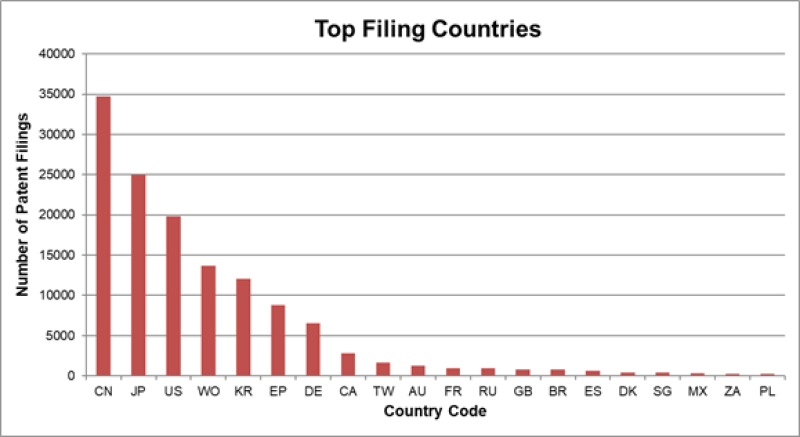
Japan and the US round out the top three countries, followed by South Korea and countries in Europe. This suggests that the prospect of successfully commercialising ‘hydrogen economy inventions’ is favourably viewed by these leading countries.
Australia’s performance
If Australia wants to stay in the hydrogen economy race, it has some catching up to do in terms of investment by local innovators into practical research, which should help increase filing numbers over time.
At present, the major applicants in Australia include a mix of companies, mainly from Asia, Europe and the US – with Sumitomo having the largest number of filings. None of the key worldwide filers such as Toyota, Honda, Hyundai and Panasonic have applied for protection in Australia. Despite Australia’s resources, this may point to the need for Australia to do more in attracting key players.

After an initial kickstart between 2000 and 2004, Australian filing numbers have also been relatively stagnant. The number remains consistent at around 100 filings per year since 2004. Likewise, the number of domestic companies filing for protection (e.g. AquaHydrex, Redflow, Hydrexia, UNSW and Monash University) continues to remain at a static rate.

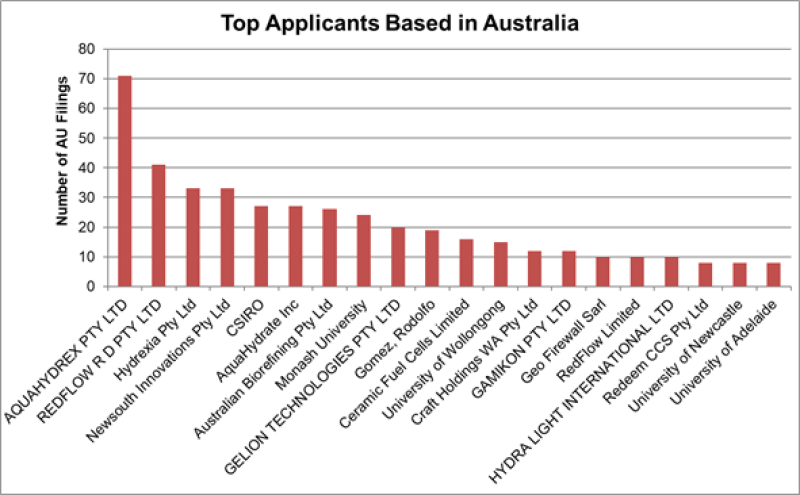

Looking at the positives, domestic companies are looking to protect their inventions globally. For example, domestic companies have a high conversion into WO (PCT) filings, and are then pursuing these filings into the US, Europe, China and Japan – all of which are major countries for the future of hydrogen development. Support from the Australian government’s National Hydrogen Strategy, which aims to position Australia’s hydrogen industry as a major player by 2030, will hopefully enhance Australia’s ‘hydrogen-patent’ output.
Growing the hydrogen economy
In terms of patenting activity, Japan and South Korea, followed by Europe, lead the world’s hydrogen economy. The world’s two biggest economies, China and the US, will be acutely aware of the status quo and it can be expected that they would adjust their output accordingly.
Put simply, if Australia wants to play a role beyond supplying the natural resources needed for production, it must refocus its research and development (R&D) agenda on hydrogen, and begin increasing its patent output.
Robert Wulff
Principal, Patent attorney, Griffith Hack
E: robert.wulff@griffithhack.com
Arun Nagasubramanian
Trainee patent attorney, Griffith Hack
E:
arun.nagasubramanian@griffithhack.com













