Design law is one of the least harmonised areas of IP, not least in the terminology used, Chris Carani of McAndrews Held & Malloy said. One issue that continues to cause difficulty is the exception, common to most laws, that covers functional attributes. Speakers from the United States, China, Brazil and the EU discussed various cases where functionality had been addressed (see images).
These cases raise two policy questions regarding functionality, said Carani: first, what is the test to establish whether a design is eligible for protection? And, second, what is the scope of protection when particular elements of a design are dictated solely by function – should any aspects of the design be disregarded?
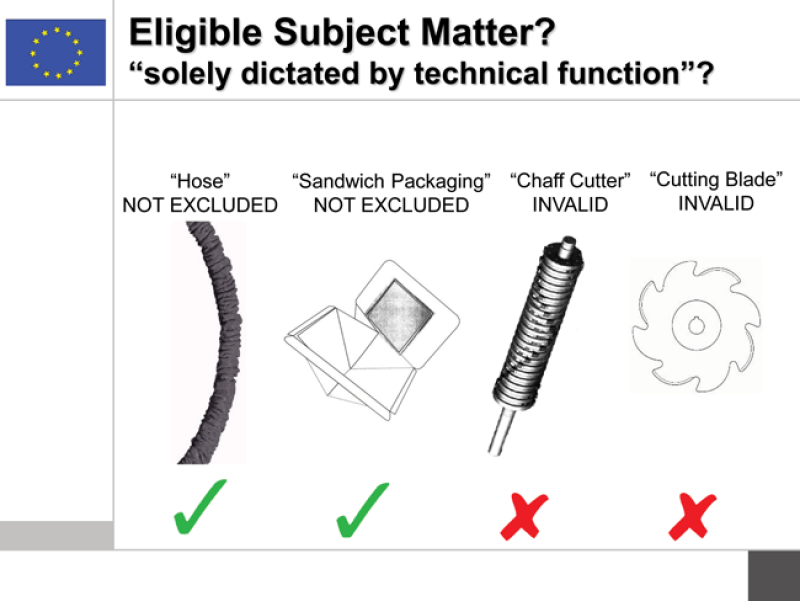
On the first, as Sara Ashby of Redd Solicitors in the UK illustrated, many tests have been proposed, including the multiplicity of forms theory, the alternative designs theory, the aesthetic consideration test and the primarily functional test. She discussed the Lindner v Franssons case, concerning industrial cutters, where the OHIM 3rd Board of Appeal said that a design is functional if its “characteristic features” pursue a purely technical function.
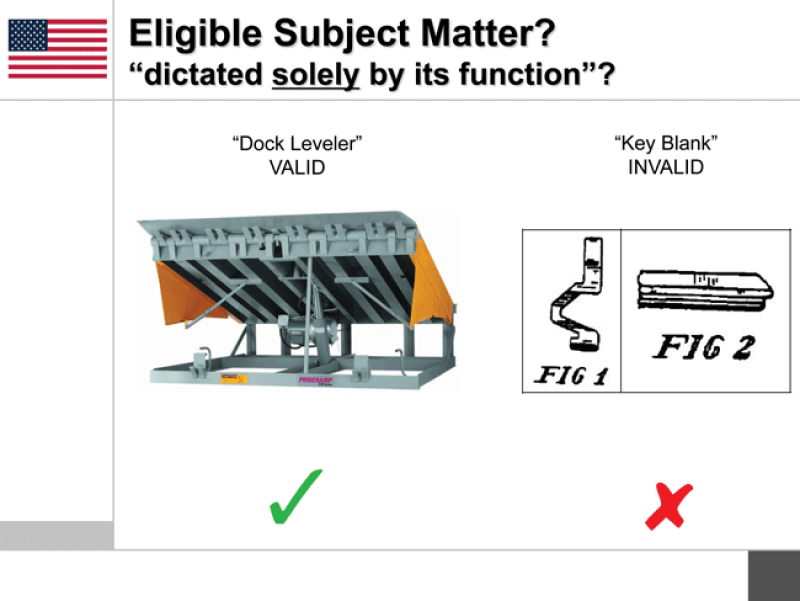
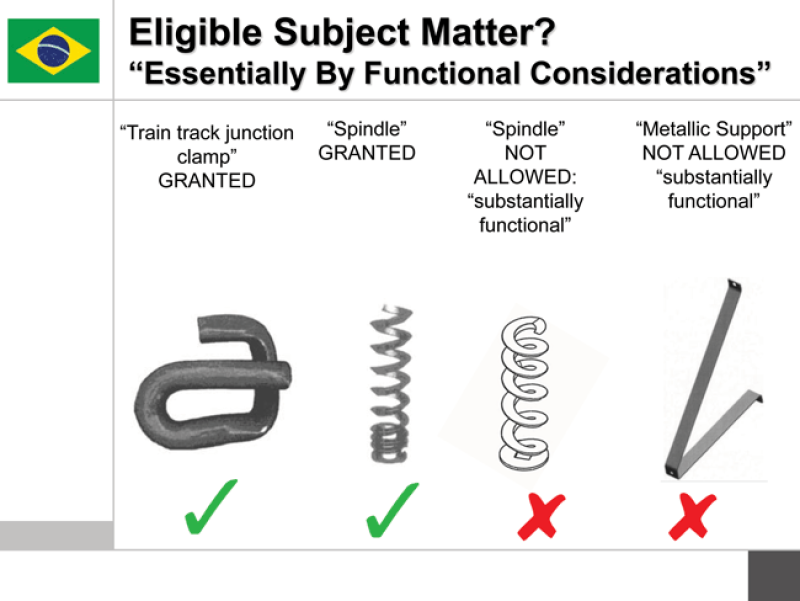
Carani said that in the US there has only been one case where the Federal Circuit has found that a design was solely dictated by function: it concerned a key blade where only the blade itself was claimed. In Brazil, said Lucas Gaiarsa of Gaiarsa Ferreira & Meyer, the statutory exceptions are clear, but he added: “The law is there but the application is not always something you understand completely.”
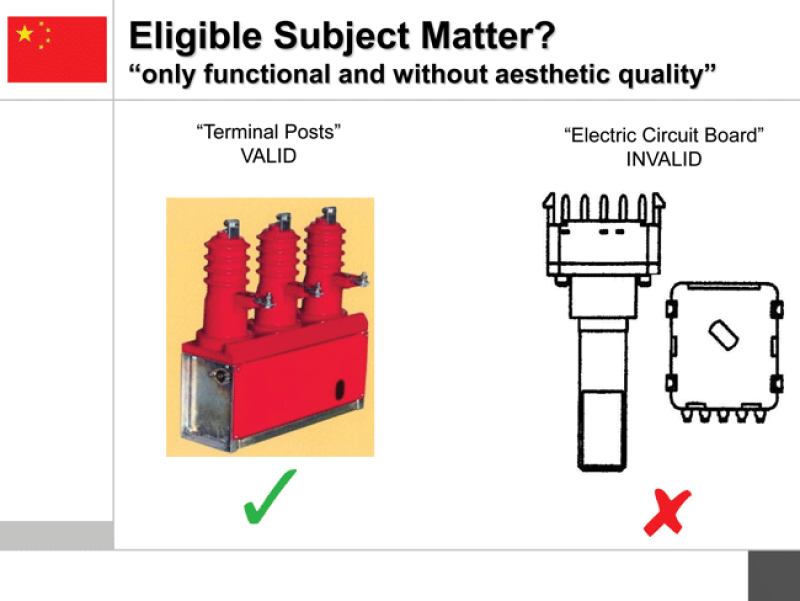
On the second question (whether to disregard aspects of the design in infringement cases), Lila Wu of CCPIT Patent and Trademark Law Office said China’s courts had been clear that “any design feature with technical function should not be considered and should be removed from the comparison of infringement”. As an example, she cited a case involving an electrical power unit, where the plug holes were held to be functional. Ashby pointed to a European dispute involving a Dyson vacuum cleaner, where a transparent bin was held to be functional (it lets you see the dirt).
Cases such as these could be examples of where “claim construction ends up being claim destruction”, said Carani. The discussion demonstrated, he added, that there is no clarity on this topic: “Hopefully AIPPI can help.” The Working Question next year is expected to cover all the relevant policy issues and tests and it may even be necessary to ask the fundamental question “Do we need a functionality exception and what are we trying to prevent?” said Carani.










